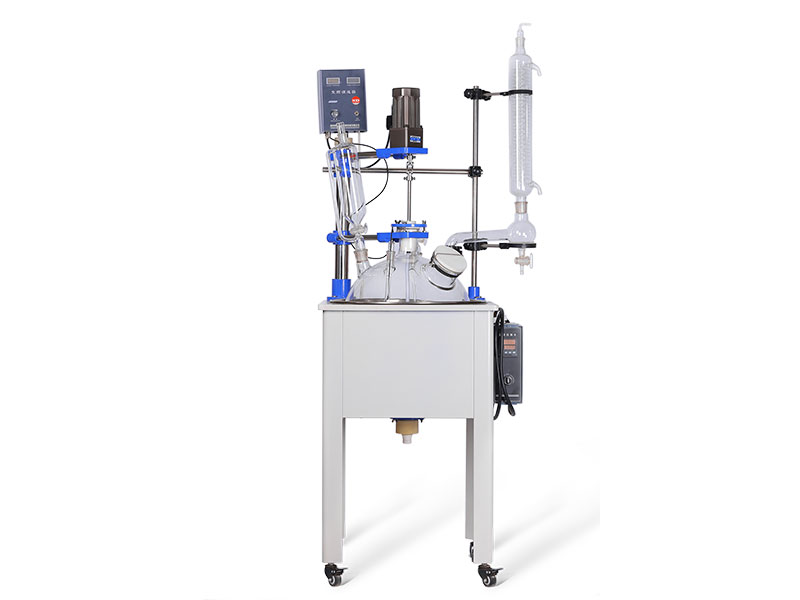
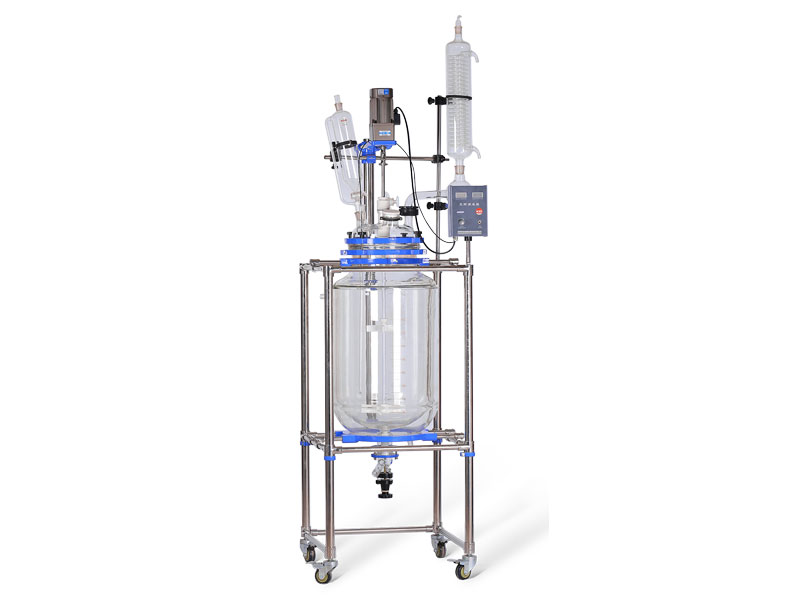
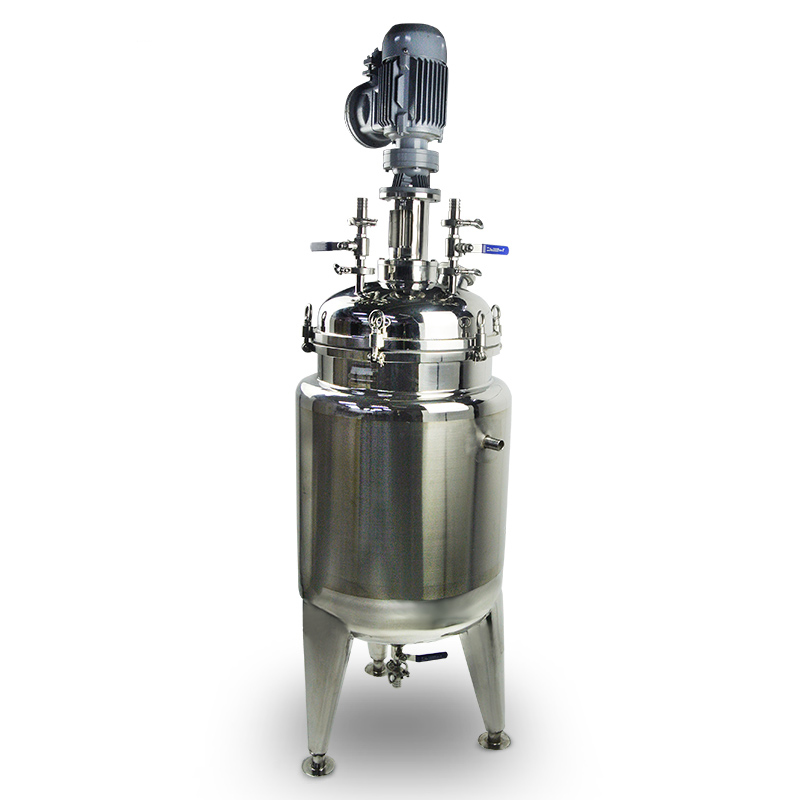
Classification and structure of reactor vessels
A glass reactor equipped with a stirrer is one of the most widely used reactors in the chemical industry. It can be used for liquid-liquid homogeneous reactions as well as heterogeneous reactions such as heterogeneous liquid phase and liquid-solid phase. , gas-liquid-solid equivalent. It is widely used in petrochemical, rubber, pesticide, dye, pharmaceutical and other industries to complete sulfonation, nitrification, hydrogenation, hydrocarbonization, polymerization, condensation and other processes. In the production of the pharmaceutical industry, almost all unit operations can be carried out in glass reactor vessels.
The scope of application of glass reactors is extensive because such reactors have a simple structure, convenient processing, high mass transfer efficiency, uniform temperature distribution, and wide controllable operating conditions (such as temperature, concentration, residence time, etc.). The operation flexibility is large, it is easy to change the variety, and it can adapt to diversified production.
Classification of glass reactor vessels
1. Classification by reactor structure
According to the reactor structure, the reactor can be divided into various reactors such as a tank type (tank type), a tube type, a tower type, a fixed bed, a fluidized bed, and a moving bed. The tank reactor is widely used and is suitable for other types of reactions in addition to the gas phase reaction. It is common to use homogeneous or non-uniform reverse phase for liquid phase. Most tubular reactors are used for gas phase and liquid phase homogeneous reaction processes, as well as gas-solid and gas-liquid heterogeneous reaction processes; fixed bed and flow. Chemical beds and moving beds are mostly used in the gas-solid phase reaction process.
2. Classified by operation mode
It is divided into batch, semi-continuous and continuous operation according to the operation mode.
a. Intermittent operation equipment is not high in utilization rate and labor intensive. It is only suitable for small batch and multi-variety production. This operation is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
b. Semi-batch operation, suitable for reactions requiring a high concentration of one reactant and a low concentration of another reactant, suitable for reactions that can control the desired reaction temperature by adjusting the feed rate.
c. Continuous stirring glass reactor, glass reactor equipment with high utilization rate, stable product quality, easy automatic control, suitable for mass production.
3. Sort by material
Divided into steel reactor, cast iron reactor and glass reactor.
a. The steel reactor is characterized by simple manufacturing process, low cost, convenient maintenance and repair, and wide application range. Therefore, chemical production is widely used. Because the material Q235A is not resistant to acid medium corrosion, a stainless steel reactor is commonly used, which can withstand general acidic medium. The mirror-polished stainless steel reactor is also particularly suitable for high viscosity system polymerization.
b. The cast iron reactor is used more in the reaction process of chlorination, sulfonation, nitration, condensation, and sulfuric acid enrichment.
c. The glass reactor is made of high borosilicate material, which has good corrosion resistance and high temperature resistance. It is widely used in the halogenation reaction in fine chemical production and various reactions in the presence of hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid and nitric acid.
1 Corrosion resistance It can resist the corrosion of most inorganic acids, organic acids, organic solvents and other media, especially in the medium of hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, aqua regia and other media.
2 heat resistance is allowed to be used in a range of 30~240 °C, the temperature difference between heat resistance is less than 120 °C, and the cold temperature difference is less than 110 °C.
3 Impact resistance and impact resistance are small, so avoid hard object impact collision when using. The glass reactor should be protected from collision during transportation and installation. When feeding, prevent heavy objects from falling into the container, and slowly pressurize and heat up during use to prevent drastic changes.
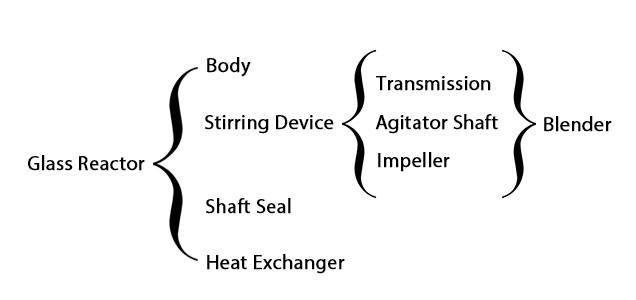
Structure diagram of glass reactor